This tutorial in the category WordPress hacking will teach you how to scan WordPress websites for vulnerabilities, enumerate WordPress user accounts and brute force passwords. Enumerating WordPress users is the first step in a brute force attack in order to gain access to a WordPress account. WPScan has the option to scan a target website to retrieve a list of account names. IN this tutorial we will also look at how to hide usernames from WPScan so you can avoid the enumeration of user accounts and limit the effectiveness of brute force attempts. We will conclude this tutorial with a demonstration on how to brute force root passwords using WPScan on Kali Linux. WPScan is an automated black box WordPress vulnerability scanner. This tool is a must have for any WordPress developer to scan for vulnerabilities and solve issues before they get exploited by hackers. Together with Nikto, a great webserver assessment tool, this tool should be part of any penetration test targeting a WordPress website or blog.
WPScan comes pre-installed on the following Linux distributions:
The latest version is WPScan 2.8 and the database currently contains:
- Total vulnerable versions: 98
- Total vulnerable plugins: 1.076
- Total vulnerable themes: 361
- Total version vulnerabilities: 1.104
- Total plugin vulnerabilities: 1.763
- Total theme vulnerabilities: 443
The Windows operation system is currently not supported by WPScan. The latest version is available for download at the following website (Linux & Mac): https://wpscan.org/
WPScan update
Start with the following command to update the WPScan vulnerabilities database:
wpscan –update
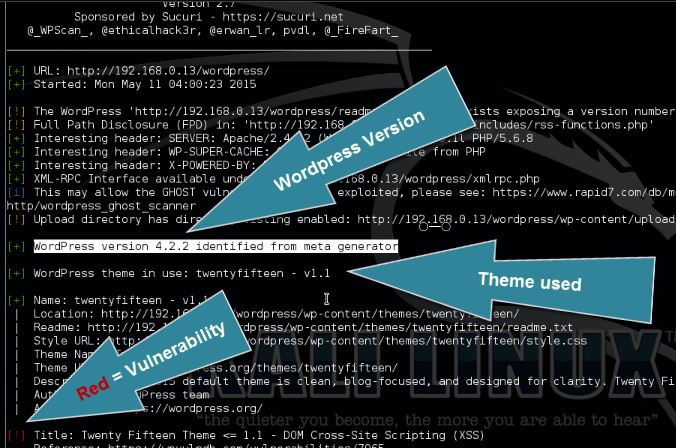
Scanning WordPress vulnerabilities
After updating the vulnerability database use the following command to scan the target website for the most popular and recent vulnerabilities:
wpscan –url [wordpress url]
How to enumerate WordPress users
The WordPress user enumeration tool is used the retrieve a list of registered WordPress users for the target host. User enumeration is the first step when an attacker wants to gain access to a specific target by brute forcing. The enumeration tool scans the target on posts, pages and custom types for authors and usernames.
Use the following command to enumerate the WordPress users:
wpscan –url [wordpress url]–enumerate u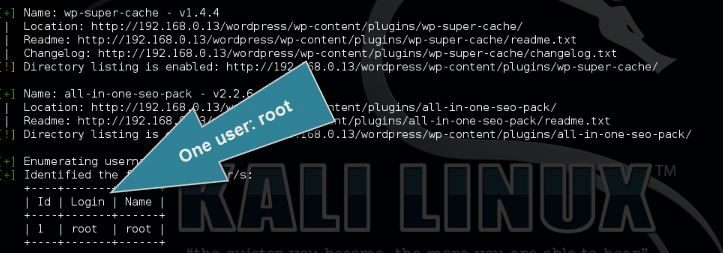
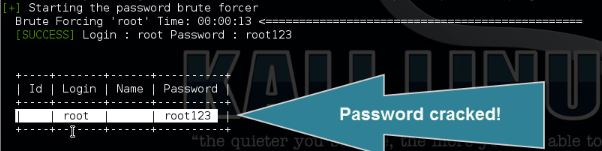
How to brute force the root password
Use the following command to brute force the password for user root:
wpscan –url [wordpress url]–wordlist [path to wordlist]–username [username to brute force]–threads [number of threads to use]
How to avoid WordPress User Enumeration
If you want to avoid WordPress user enumeration, you should avoid using the username as nickname and display name which is shown publicly in WordPress. The best option is to choose an administrator username which consists of random characters and use a different nickname. WPScan scans for usernames in the URL’s so if you won’t use the username it cannot be scanned by WPScan. Another way to prevent user enumeration is to use a different account to publish posts and answer to replies.
How to avoid Wordpres password brute forcing
The best way to keep attackers using brute force methods out is to limit the login attempts for and IP address. There are several plug-ins available for WordPress to limit the number login attempts for a specific username and IP, such as Wordfence. The latest WordPress versions have the option to limit login attempts by default. Make sure you limit entries to a maximum of 3 and increase lock out time a lot after 2 lock outs (which is 6 password attempts).
WordPress hacking Video Tutorial
Thanks for watching and please subscribe to my YouTube channel for more hacking tutorials :)
Enumeration Arguments
Fin below an overview of enumeration arguments which can be used for scanning:
–enumerate | -e [option(s)] Enumeration.
option :
u – usernames from id 1 to 10
u[10-20] usernames from id 10 to 20 (you must write [] chars)
p – plugins
vp – only vulnerable plugins
ap – all plugins (can take a long time)
tt – timthumbs
t – themes
vt – only vulnerable themes
at – all themes (can take a long time)
Multiple values are allowed : “-e tt,p” will enumerate timthumbs and plugins
If you’re interested in learning more about web penetration testing you can follow any of these online courses:
Hacking Courses on Udemy
Bug Bounty – An Advanced Guide to Finding Good Bugs
Real World Bug Bounty Techniques

Website Hacking / Penetration Testing & Bug Bounty Hunting
Become a bug bounty hunter! Hack websites & web applications like black hat hackers and secure them like experts.


22 Comments
Thank you fer this verry well article and your work.
Nice but what wordlist did you use, I am trying one called rockyou.txt but I am not sure the best to try
thanks
There are many wordlist available for download but you can also make your own using tools like Crunch. Check out this tutorial: http://www.hackingtutorials.org/general-tutorials/crunch-password-list-generation/
hi, there is a security plugging for non listing users there is a scrip for stopping it, how do i use it tnx
Getting error
” local_vulnerable_files.xml: checksums do not match ”
Need help
Thanks
which version used in this article?
I want to start testing my clients websites but when i run wpscan on the usernames with brute force it drops the connection for a period of time. is there a way to have wpscan keep testing and checking passwords in the text file?
Most recent WordPress installations contain some sort of brute force protection to ban IP’s with too many failed login attempts.
You are on a wrong way if you want to test your clients with wpscan. Wpscan is just a application and isn’t very strong, I`d recommend you using other Tools than wpscan
Hi all,
Thank for all these tutorials they are really useful.
I am having the following issue when I use socks 5:
Every argument works fine for me and I am able to retrieve usernames but when I add the argument ‘–proxy socks5://127.0.0.1:9000’ it always give me a ‘target seems to be down’.
Any idea of what could be going on? I am a 100% sure that the server is up as I can reach it without the –proxy argument.
Cheers,
Owl
how can i install wordPress in windows or kalli for pen testing please ?
On Kali Linux you have an Apache web server installed. You can start Apache using the following command:
service apache2 start
Then download WordPress to the following directory:
/var/www/html
From here you need to follow the WordPress installation manual. The manual includes which dependencies are needed, how to configure SQL and the database etc.
On Windows I would recommend you to use XAMPP.
Great article!
If you create a website on WordPress, would it be legal and within the ToS to try hacking your own site?
If you’re installing WordPress on a server that you own, or even better install it locally, it’s perfectly legal.
Plugins is not good way to protect against brute force. Plugins still using processor to block any attempts. The best way is using .htaccess and lock REST API (ofcourse if you dont use it)
Thank you for your comment! This article needs an update after 2 years, I will definitely take your suggestions into account.
Hi everyone, the problem is the reliable word list! do you know where to find some good word list? thank you
Hi,
Checkout SecLists for a lot of good wordlists: https://github.com/danielmiessler/SecLists
Best regards,
Hacking Tutorials
the target is responding with 403
any solve??
A good article, its informative and the key points are helpful to prevent WordPress website from hacking. It will be great if you share some other methods of hacking WordPress site, besides brute forcing.
Hi,
Is there any way to not use wordlist file instead we generate and test at a same time?